Dans les articles précédents, nous avons vu comment utiliser Magisk, exploré le contenu d’une mise à jour Android puis l’on s’est fait une idée de la démarche suivie par Magisk pour fournir des droits root à une application arbitraire.
On sait que rooter un téléphone avec Magisk implique une modification d’une partition (init_boot dans notre cas).
Mais comment l’application Magisk réalise-t-elle ces modifications ?
Modification de l’init_boot.img par Magisk
Lorsque l’on patche l’image init_boot.img avec Magisk, les messages suivants sont affichés :
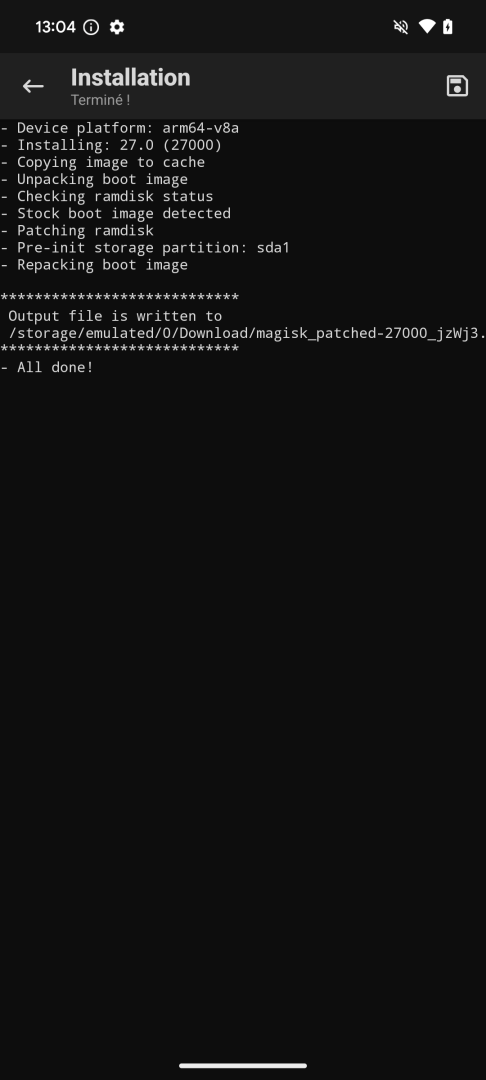
Partons de ces messages pour débobiner la pelote de laine.
Les deux seules occurrences du message « Unpacking boot image » se trouvent dans les scripts boot_patch.sh et uninstaller.sh.
Ce dernier ne contient toutefois pas le message « Repacking boot image », contrairement à boot_patch.sh, si bien que c’est le script boot_patch.sh qui va nous intéresser.
Notons que ce script commence par un commentaire récapitulant les rôles des différents utilitaires Magisk, ce qui est tout à fait appréciable :
# File name Type Description
#
# boot_patch.sh script A script to patch boot image for Magisk.
# (this file) The script will use files in its same
# directory to complete the patching process.
# util_functions.sh script A script which hosts all functions required
# for this script to work properly.
# magiskinit binary The binary to replace /init.
# magisk binary The magisk binary.
# magiskboot binary A tool to manipulate boot images.
# init-ld binary The library that will be LD_PRELOAD of /init
# stub.apk binary The stub Magisk app to embed into ramdisk.
# chromeos folder This folder includes the utility and keys to sign
# (optional) chromeos boot images. Only used for Pixel C.Notons d’abord que le premier argument, $1, est le chemin du fichier à patcher :
BOOTIMAGE="$1"
[ -e "$BOOTIMAGE" ] || abort "$BOOTIMAGE does not exist!"On unpack ensuite le bootimage avec magiskboot :
#########
# Unpack
#########
CHROMEOS=false
ui_print "- Unpacking boot image"
./magiskboot unpack "$BOOTIMAGE"Le commentaire ci-dessus nous dit que magiskboot est un « tool to manipulate boot images ». Mais encore ?
Regardons le help de magiskboot pour avoir des précisions. Le texte pondu par magiskboot help étant assez long, nous ne retiendrons que la liste des commandes proposées :
unpack bootimg: extrait les différents composant du fichierbootimgrepack origbootimg outbootimg: recréé un fichieroutbootimgà partir des éléments deorigbootimgverify bootimg: vérifie la signature debootimg, retourne 0 (succès) ou 1 (échec)sign bootimg: signebootimgextract payload.bin partition outfile: extrait la partitionpartitiondu fichierpayload.bin, dans le fichieroutfilehexpatch file hexpattern1 hexpattern2: recherche le motifhexpattern1dansfileet le remplace parhexpattern2cpio incpio commands: exécute la sequence de commandes cpiocommandssur le fichierincpiodtb file action: réalise des actions en lien avec le dtb, ie le device tree blobsplit file: splitte un fichier .dtbcompress=format infile outfile: compresse un fichierdecompress infil outfile: décompresse un fichier
La commande magiskboot unpack "$BOOTIMAGE" réalise donc l’extraction de l’init_boot.img…comme le commentaire le laissait penser.
Que ce passe-t-il dans la suite du script ?
Si un fichier ramdisk.cpio est présent, le script teste sa décompression avec magiskboot cpio ramdisk.cpio test :
###################
# Ramdisk Restores
###################
# Test patch status and do restore
ui_print "- Checking ramdisk status"
if [ -e ramdisk.cpio ]; then
./magiskboot cpio ramdisk.cpio test
STATUS=$?
SKIP_BACKUP=""
else
# Stock A only legacy SAR, or some Android 13 GKIs
STATUS=0
SKIP_BACKUP="#"
fiLa valeur de retour de cette commande est soit 0 (cas nominal), soit 1 (ramdisk.cpio patché avec Magisk), soit 2 (format non supporté), soit 4 (ramdisk.cpio Sony).
Dans le cas normal, l’init_boot.img est copié dans stock_boot.img et le ramdisk.cpio est copié dans ramdisk.cpio.orig.
case $STATUS in
0 )
# Stock boot
ui_print "- Stock boot image detected"
SHA1=$(./magiskboot sha1 "$BOOTIMAGE" 2>/dev/null)
cat $BOOTIMAGE > stock_boot.img
cp -af ramdisk.cpio ramdisk.cpio.orig 2>/dev/null
;;le cas d’un ramdisk.cpio patché avec Magisk, est géré différemment :
1 )
# Magisk patched
ui_print "- Magisk patched boot image detected"
./magiskboot cpio ramdisk.cpio \
"extract .backup/.magisk config.orig" \
"restore"
cp -af ramdisk.cpio ramdisk.cpio.orig
rm -f stock_boot.img
;;enfin en cas d’echec l’exécution s’arrête :
2 )
# Unsupported
ui_print "! Boot image patched by unsupported programs"
abort "! Please restore back to stock boot image"
;;
esacDurant l’étape suivante, le script compresse les fichiers magisk, stub.apk et init-ld :
#################
# Ramdisk Patches
##################
ui_print "- Patching ramdisk"
$BOOTMODE && [ -z "$PREINITDEVICE" ] && PREINITDEVICE=$(./magisk --preinit-device)
# Compress to save precious ramdisk space
./magiskboot compress=xz magisk magisk.xz
./magiskboot compress=xz stub.apk stub.xz
./magiskboot compress=xz init-ld init-ld.xzUn fichier config contenant divers éléments de configuration est créé :
echo "KEEPVERITY=$KEEPVERITY" > config
echo "KEEPFORCEENCRYPT=$KEEPFORCEENCRYPT" >> config
echo "RECOVERYMODE=$RECOVERYMODE" >> config
if [ -n "$PREINITDEVICE" ]; then
ui_print "- Pre-init storage partition: $PREINITDEVICE"
echo "PREINITDEVICE=$PREINITDEVICE" >> config
fi
[ -n "$SHA1" ] && echo "SHA1=$SHA1" >> configEnsuite, le ramdisk.cpio est patché :
./magiskboot cpio ramdisk.cpio \
"add 0750 init magiskinit" \
"mkdir 0750 overlay.d" \
"mkdir 0750 overlay.d/sbin" \
"add 0644 overlay.d/sbin/magisk.xz magisk.xz" \
"add 0644 overlay.d/sbin/stub.xz stub.xz" \
"add 0644 overlay.d/sbin/init-ld.xz init-ld.xz" \
"patch" \
"$SKIP_BACKUP backup ramdisk.cpio.orig" \
"mkdir 000 .backup" \
"add 000 .backup/.magisk config" \
|| abort "! Unable to patch ramdisk"
rm -f ramdisk.cpio.orig config *.xzDans l’étape suivante, fstab est patché :
#################
# Binary Patches
#################
for dt in dtb kernel_dtb extra; do
if [ -f $dt ]; then
if ! ./magiskboot dtb $dt test; then
ui_print "! Boot image $dt was patched by old (unsupported) Magisk"
abort "! Please try again with *unpatched* boot image"
fi
if ./magiskboot dtb $dt patch; then
ui_print "- Patch fstab in boot image $dt"
fi
fi
doneLorsqu’un noyau est présent dans le fichier fourni (ce qui n’est pas le cas avec un init_boot.img), celui-ci est patché si nécessaire :
if [ -f kernel ]; then
PATCHEDKERNEL=false
# Remove Samsung RKP
./magiskboot hexpatch kernel \
49010054011440B93FA00F71E9000054010840B93FA00F7189000054001840B91FA00F7188010054 \
A1020054011440B93FA00F7140020054010840B93FA00F71E0010054001840B91FA00F7181010054 \
&& PATCHEDKERNEL=true
# Remove Samsung defex
# Before: [mov w2, #-221] (-__NR_execve)
# After: [mov w2, #-32768]
./magiskboot hexpatch kernel 821B8012 E2FF8F12 && PATCHEDKERNEL=true
# Disable Samsung PROCA
# proca_config -> proca_magisk
./magiskboot hexpatch kernel \
70726F63615F636F6E66696700 \
70726F63615F6D616769736B00 \
&& PATCHEDKERNEL=true
# Force kernel to load rootfs for legacy SAR devices
# skip_initramfs -> want_initramfs
$LEGACYSAR && ./magiskboot hexpatch kernel \
736B69705F696E697472616D667300 \
77616E745F696E697472616D667300 \
&& PATCHEDKERNEL=true
# If the kernel doesn't need to be patched at all,
# keep raw kernel to avoid bootloops on some weird devices
$PATCHEDKERNEL || rm -f kernel
fiEnfin l’init_boot.img est reconstruit avec le ramdisk modifié :
#################
# Repack & Flash
#################
ui_print "- Repacking boot image"
./magiskboot repack "$BOOTIMAGE" || abort "! Unable to repack boot image"
# Sign chromeos boot
$CHROMEOS && sign_chromeos
# Restore the original boot partition path
[ -e "$BOOTNAND" ] && BOOTIMAGE="$BOOTNAND"
# Reset any error code
trueConclusions
Le script boot_patch.sh lancé par l’application Magisk modifie l’init_boot.img :
- Ajout de l’init sauce Magisk
- Ajout d’un répertoire overlay.d contenant notamment magisk.xz, stub.xz